[introduction] in the process, the heat exchanger of various types of equipment is essential, then according to the different craft production process and production scale, design investment, low energy consumption, high heat efficiency, convenient maintenance of the heat exchanger is a very important job.
Heat exchanger classification
According to process function classification
Cooler, heater, reboiler, condenser, evaporator and Superheater, waste heat boiler etc..
Classification by means of heat transfer and structure
A direct contact type heat transfer and heat transfer, the heat transfer of wall type is divided into tube shell type heat exchanger, plate type, tube type, film type and other forms of.
Two, from the process of selection of heat exchanger
cooler
1, recuperative cooler
(1) when the heat flux is large, can choose the plate heat exchanger area and heat transfer coefficient of the economy, but the temperature of plate heat exchanger is generally not more than 150 DEG C, pressure drop.
(2) for pressure drop and high temperature pressure, the choice of shell and tube heat exchanger is more reasonable.
(3) the plate fin heat exchanger, due to the role of the fin, suitable for cooling gas materials, the use of temperature is generally less than 150.
(4) air cooler is suitable for high temperature and high pressure process conditions, the temperature of the heat flow outlet is higher than the design temperature of 15~20.
2, direct contact type cooler
It is suitable for the temperature of the process material, the cooling of the process material, the cooling of a large amount of hot water and the cooling of a large amount of water vapor.
heater
1, high temperature
When the temperature requirement is as high as 500 degrees Celsius, the heat storage type or direct thermal power heating can be used.
2, middle temperature conditions
The organic heat carrier as the heating medium is generally used for 150~300 C condition. Divided into two kinds of liquid phase and gas phase.
3, low temperature
When the temperature is less than 150 DEG C when the first consider the selection of shell and tube heat exchanger, only special craft material characteristics or process conditions, before considering other forms, such as heat sensitive material with falling film type or corrugated plate heat exchanger.
Re boiling device

Figure four 1 types of re boiling device
The use of tube shell heat exchanger, divided into forced circulation type, thermal siphon and reboiler three. The design of the temperature difference between the general selection of 20~50 degrees Celsius, one-way evaporation rate is generally 10%~30%.

Table 1 Comparison of various kinds of re boiling apparatus
condenser
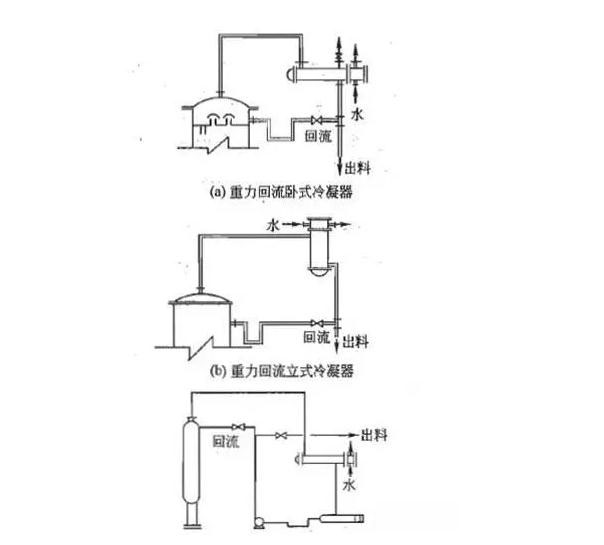
Fig. 2 condenser form
Generally used for condensation of steam condensation and distillation tower of reaction gas, the distillation tower overhead, general selection of shell and tube type, air cooler, spiral plate, plate fin heat exchanger as the condenser, the reaction system, general selection of shell and tube type, sleeve type or spray type heat exchanger as the condenser.

Table 2 Comparison of characteristics of condenser
Three, commonly used in heat exchanger - shell and tube heat exchanger

Fig. 3 shell and tube heat exchanger
process conditions
1, temperature
Cooling water outlet temperature should not be higher than 60 degrees Celsius in order to avoid serious fouling, high temperature temperature should not be less than 20 degrees Celsius, the temperature should not be less than 5. When the heat transfer between the two processes, the temperature difference at the low temperature should not be less than 20.
The outlet temperature of the cooling water should not be higher than the temperature of the process fluid when the single shell side heat exchanger is used and the water is used as a coolant. The coolant inlet temperature should be higher than the freezing point in the process flow. When the material with inert gas is condensed, the outlet temperature of the coolant should be lower than the dew point of the process material.
2, pressure drop
Increasing the flow rate of the process flow can increase the heat transfer coefficient, which makes the structure of the heat exchanger compact, but the flow rate increases with the pressure drop of the heat exchanger.
3, logistics arrangements
In order to save the thermal insulation layer and reduce the thickness of the shell, high temperature logistics generally take the process, sometimes for the material cooling can also make the high temperature logistics go shell.
High pressure logistics process.
The larger viscosity of the logistics process, the shell side can get a higher heat transfer coefficient.
Strong corrosion of the logistics process.
There are specific requirements for the pressure drop of the process logistics process, because of the heat transfer coefficient and pressure drop calculation error is small.
The dirty and easy to scale logistics through the tube side, easy cleaning and controlling scale, if you take the shell, the tube row square, and adopts a detachable type heat exchanger.
Less flow of the logistics process, easy to form a turbulent flow of the logistics to increase the heat transfer coefficient.
The heat transfer film coefficient is smaller, and the logistics process is easy to increase the heat transfer coefficient.
Structure parameter
1, smooth tube
Diameter: the smaller the diameter of the heat exchanger, the more compact, more expensive, while the greater the pressure drop. Commonly used in the diameter of 19mm, 25mm, 32mm.
Length: no phase change heat pipe, the heat transfer coefficient increases, the longer, the heat exchange area of the same, with long tube side and less number of small pressure drop, heat transfer area and low price.
Arrangement: there are mainly two kinds of square and triangular distribution form, distribution of triangle turbulent shell for logistics, the square cloth for cleaning in shell side. The smaller the pipe center distance, the more compact the equipment, but it will cause the tube plate to be thickened, the cleaning is inconvenient, the shell side pressure drop is increased, and the distance between the 1.25~1.5 diameter of the pipe is generally used.
2, the number of tube and shell form
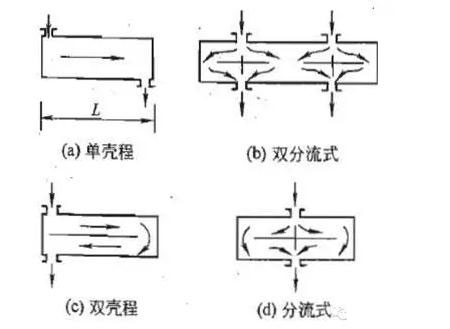
Fig. 4 shell form
Commonly used there are 1, 2 tube or 4 tube, the number of pipe increases, the pipe flow rate increases, but the tube flow rate to be subject to the limit of pipe pressure drop. Shell form is divided into single shell, double split type, double shell and split type.
3, baffle plate
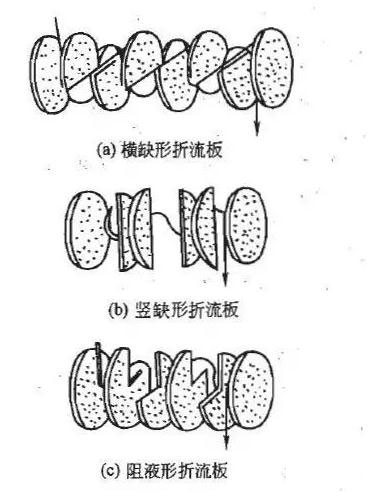
Fig. 5 the form of round and short baffle
The baffle plate can change the direction of the shell side fluid, which is perpendicular to the tube bundle to obtain a better heat transfer effect. Generally divided into round and short type baffle plate, annular disc type baffle plate and hole type baffle plate. The baffle spacing affects the flow direction and the flow rate of the shell side flow, which influences the heat transfer efficiency. The minimum baffle spacing for the shell diameter of 1/5, should not be less than 50mm.
Four, commonly used in heat exchanger - plateHeat exchanger

Figure 6 heat exchanger
Basic structure
The main heat exchanger type frame (detachable) and brazing type two categories, with a herringbone corrugated plate, corrugated board and the level of flat plate shaped aneurysm three main plate form.
Operating principle
Heat exchanger is a new type of high efficient heat exchanger is composed of a metal plate with corrugated laminations loaded into the structure which comprises a gasket, a pressing plate (movable end plate and fixed end plate) and the frame (upper and lower guide rod, the front pillar).
The plate between the seal and diversion by sealing gasket, separating the cold / hot two fluid passages, cold / heat exchange medium respectively through the heat exchange in the respective channels, and between the plates, to achieve the user required temperature.
Characteristic
High heat transfer efficiency
Safe and reliable use
Small footprint, easy to maintain
Adjust to changing circumstances
Is conducive to the use of low temperature heat source
Less resistance loss
Small cooling water
Low investment efficiency
application area
refrigeration
HVAC
chemical industry
metallurgical industry
Machinery industry
Power industry
paper industry
textile industry
food industry
Grease Technology
Central heating
Five, commonly used in heat exchanger - tube type heat exchanger
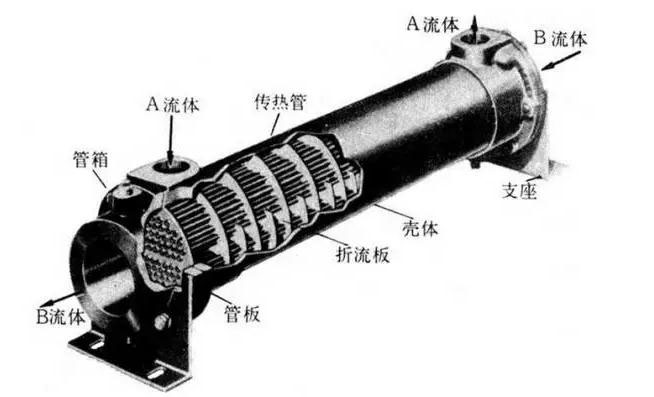
Fig. 7 tube heat exchanger
Basic structure
The utility model is mainly composed of a shell, a tube bundle, a tube plate and a head. The shell is round, and the inner part is provided with parallel tubes, and the two ends are fixed on the tube plate.
classification
Fixed tube plate
floating head
“ U” type tube
Operating principle
An inlet nozzle of the head end of the working substance is in the heat transfer pipe, and the process can realize a pipe path, a two pipe and a four pipe structure according to the process requirements.
The other working substance is arranged in the shell body at one end of the shell and evenly distributed in the heat transfer tube, and the flow state can be arranged in different types and amounts of baffle plates according to the process requirements.
As the heat transfer element — — heat pipe, brass tube can be used according to the technological requirements, copper fin tube and steel tube, so as to ensure the working fluid of different physical properties and different temperature exchange in the heat exchanger heat, to achieve the purpose of cooling or heating.
Process equipment network finishing release, reproduced please indicate the source








