Corrosion prevention measures for chemical equipment
Classification of chemical equipment corrosion
The destruction of material and its surroundings.
Corrosion can be divided into metal corrosion and nonmetal corrosion.
According to the surface morphology, the corrosion is divided into general corrosion and local corrosion. The local corrosion has the small hole corrosion, stress corrosion cracking, crevice corrosion, galvanic corrosion, wear corrosion and so on;
Metal corrosion can be divided into physical corrosion, chemical corrosion and electrochemical corrosion.
Physical corrosion: the destruction of the physical function of the material, usually caused by dissolution, infiltration, such as the dissolution of molten metal containers, high temperature molten salt, molten alkali dissolution and penetration of the container.
Chemical corrosion: a direct chemical reaction between a metal and a non electrolyte. No current is produced during the corrosion process. The corrosion process is a pure oxidation reduction reaction, the corrosion medium and the metal surface atoms collide directly to form the corrosion products.
Electrochemical corrosion: the damage caused by the electrochemical reaction between metal and electrolyte solution. In the process of reaction, the electrons and electrons flow from the anode and the cathode are obtained.
Two, chemical equipment corrosion prevention measures
At present, the anti-corrosion technology mainly includes: the development of corrosion resistant materials, surface anti-corrosion technology, electrochemical protection, etc.
1) development of corrosion resistant materials
The development and research of corrosion resistant materials is a breakthrough in the progress of anti-corrosion technology. Corrosion resistant materials are mainly divided into metal materials, polymer materials, inorganic non-metallic materials.
Metal and alloy materials are the main body of structural materials, of which steel occupies a dominant position, but the corrosion resistance of steel has limitations. The development and application of high performance alloy and nonferrous metal materials have been developed rapidly, which can solve the problem of local corrosion and corrosion in special environment. For example, high corrosion resistant alloy, duplex stainless steel, high purity ferritic stainless steel, nickel base alloy, low alloy steel, titanium and titanium alloy. Corrosion resistant nonmetallic materials are widely used in chemical industry at home and abroad. Non metallic materials have excellent corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties can be improved by means of strengthening, in some areas has been developed to replace the trend of steel. Now being developed, such as: corrosion resistant plastics, glass fiber reinforced plastic, graphite, glass lining, engineering ceramics
2) surface corrosion protection technology
In the existing corrosion prevention methods, the cost of surface corrosion resistant coating and metal surface technology accounts for about 87% of the total corrosion resistance. It is an essential way to improve the service life, reduce maintenance costs and improve the level of equipment management by adopting the correct surface erosion control technology. At the same time, the corrosion resistance of the whole material is greatly improved by adopting the surface corrosion protection technology. Commonly used in chemical and petrochemical surface corrosion prevention technology, including coating, lining, plating, infiltration and the development of a variety of high-tech in recent years, which is widely used in coating and lining.
3) corrosion resistant coating

The development of corrosion resistant coatings has been the focus of people's attention. In the chemical industry, corrosion resistant coatings are mainly used in the inner and outer walls of buildings, structures, devices and storage tanks, as well as water, oil and gas pipelines. According to statistics, the corrosion of the coating, the substrate surface treatment is about 75%, therefore, it is urgent to attach importance to the quality of surface treatment. Some of the most promising coatings, such as zinc rich coatings, heavy duty coatings, high temperature resistant coatings, ceramic coatings, rust coatings, fluorocarbon coatings and so on, are the most popular coatings in the world.
4 equipment surface engineering technology
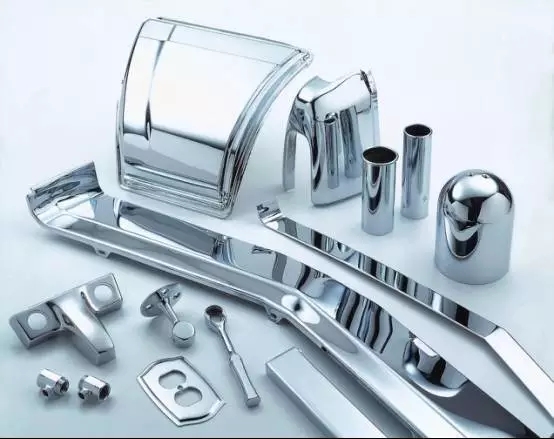

Electroplating, electroless plating in the application of chemical corrosion prevention, the main plating chromium, zinc and nickel plating.
Passivation of galvanized layer is a very active area, launched nearly ten years of low chromium or chromium free passivation, black passivation, army green passivation and strong passivation (composite passivation layer containing silicon resin or other resin), the corrosion resistance of zinc coating in marine atmosphere, industrial environment and industrial water, river environment is greatly improved. Electroless plating is a kind of film forming technology by using metal salt and reducing agent in the same solution. Electroless nickel phosphorus alloy and three nickel alloy, the product has better corrosion resistance and greater choice than the electroplating products, is one of the fastest growing surface treatment process at home and abroad.
Spray coating is a kind of technology for obtaining metal, alloy, inorganic and organic corrosion resistant and wear resistant surface layer by using flame, plasma and arc spraying.

Chemical heat treatment, chemical heat treatment, especially Aluminizing and chromizing, has been widely used in the chemical corrosion prevention of chemical industry in the past more than and 10 years.
Phosphating phosphating, as an important pretreatment process, has been used for many years. In the past more than and 10 years, the alkali metal of low temperature or room temperature phosphating of the three element system has made the progress of phosphating technology.

5) electrochemical corrosion resistance
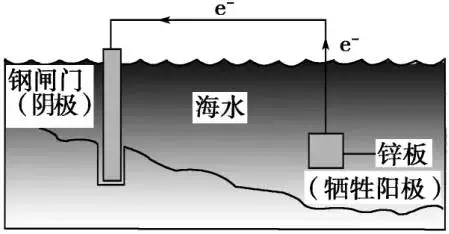
Electrochemical protection refers to the use of external current to make the metal (including alloy) corrosion potential change to reduce the corrosion rate of anti-corrosion technology. Electrochemical protection can be divided into cathodic protection and anode protection.
Electrochemical protection technology has been paid more and more attention and application in the field of chemical corrosion protection. It is a kind of effective, economical and practical method. Cathodic protection is a sufficient cathode current on the surface of the metal, which causes the metal potential to become negative, and the metal dissolution rate decreases. The structure and shape of the protected equipment should not be too complex, the structure of the complex equipment in the vicinity of the auxiliary anode current density, away from the auxiliary anode current density is small, not enough protection current. Can not even protect, resulting in the so-called “ shadowing phenomenon ”.
Cathodic protection is mainly used in metal structures in water and soilHowever, it must be used in the environment with simple structure and less corrosive medium. Cathodic protection can not only prevent the general uniform corrosion, but also can prevent the pitting corrosion, intergranular corrosion, impact corrosion and selective corrosion of some materials.
Anode protection is metal component will be protected and connected with the positive DC power supply, the metal components in the electrolyte solution to the anodic polarization potential, to establish and maintain a stable passive state, thus inhibited the anodic dissolution, the corrosion rate decreased significantly, the equipment is protected. There is no passivation characteristics of metal anode protection, can not be used.
Mainly used in:
Sulfuric acid in the production of structures, such as carbon steel tanks, a variety of heat exchangers, three sulfur generator, etc..
Structure of ammonia water and ammonium salt solution, carbonization tower, ammonia storage tank, etc..
In the strong oxidizing medium to consider using anodic protection; in both the anodic protection, but also can be used for cathodic protection, and the protective effect of two similar cases, priority should be given to the cathodic protection; if hydrogen embrittlement can not be ignored, should adopt anodic protection.
The sources of information: the belated effort chemical Forum





