The development of chemical industry park has become the key to the change of chemical industry. Among them, the major crisis of the park has always been the top priority. What are the major crises in chemical industry parks? What is the truth behind the major crisis? How can we improve the safety management of chemical industry park? With these three key questions, let's go into today's wonderful content!
Understanding the Current Situation of Major Crisis in Chemical Industry Park from Three Aspects
With the increasing demand for chemical products, the development of China's chemical industry continues to advance, forming a boom in the construction of chemical industry parks. Chemical industry park is the gathering place of chemical industry enterprises. There are many kinds of dangerous chemicals in the park, which are dense and easy to cause major crisis events, resulting in huge property losses, casualties and environmental pollution.
In recent years, what are the characteristics of the major crisis situation in China's chemical industry parks? We will interpret it from three aspects:

1. Time
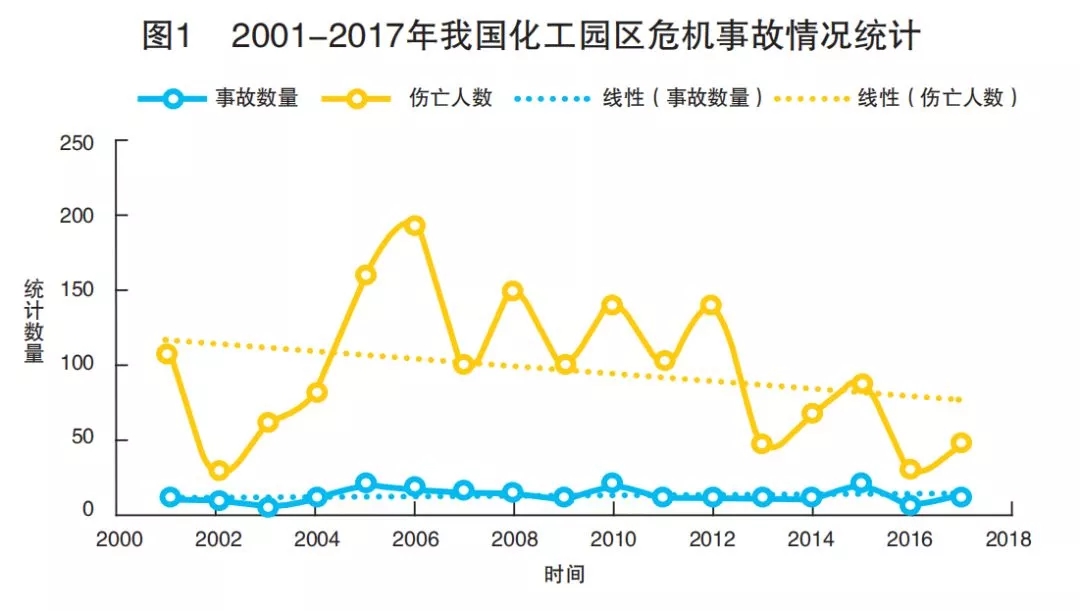
According to the statistical analysis of the data collected from the website of the Ministry of Emergency Management, China Chemical Industry Network and China Statistical Yearbook, the results show that since the new century, the development trend of major crisis accidents in China's chemical industry parks has not been significantly alleviated, and the average number of casualties has reached 12.7 pieces per year (see Figure 1). Although the casualties have declined slightly in general, the accompanying waves still exist. It is highly dynamic (variance value is 9.17), showing a high degree of uncertainty.
Summary: As an important part of urban construction, the management of chemical industry parks in China has entered a blind area to a certain extent, that is, it only pays attention to the technical optimization in the production safety process, but neglects to manage the vulnerability and controllability of chemical industry crisis accidents from the system control level.
2. Viewing from Regional Layout
According to the regional distribution of chemical parks in China, most of the large-scale chemical parks above the provincial level are located in the coastal provinces of Shandong, Hebei and Guangdong, accounting for 20% of the total number of chemical parks in China.
In terms of seven geographical regions (see Fig. 2), East China is the dominant region with 472 chemical parks, 104 at the national level, 368 at the provincial level and below; 165, 147 and 121 in North China, Central China and Northwest China, respectively; and 103, 94 and 83 in Southwest, South China and Northeast China, respectively.

By 2017
There are two main reasons for such a layout:
First, there are many coastal cities in East China, which provide geographic basis for the construction and operation of chemical industry parks.
Second, the economic development in East China has promoted the growth of people's demand for chemical products.
Because of the different economic base, emergency disposal level and geographic base, and the different potential external risks of the park, the regional distribution of casualties caused by crisis accidents in China's chemical industry parks in the past 18 years is also different.
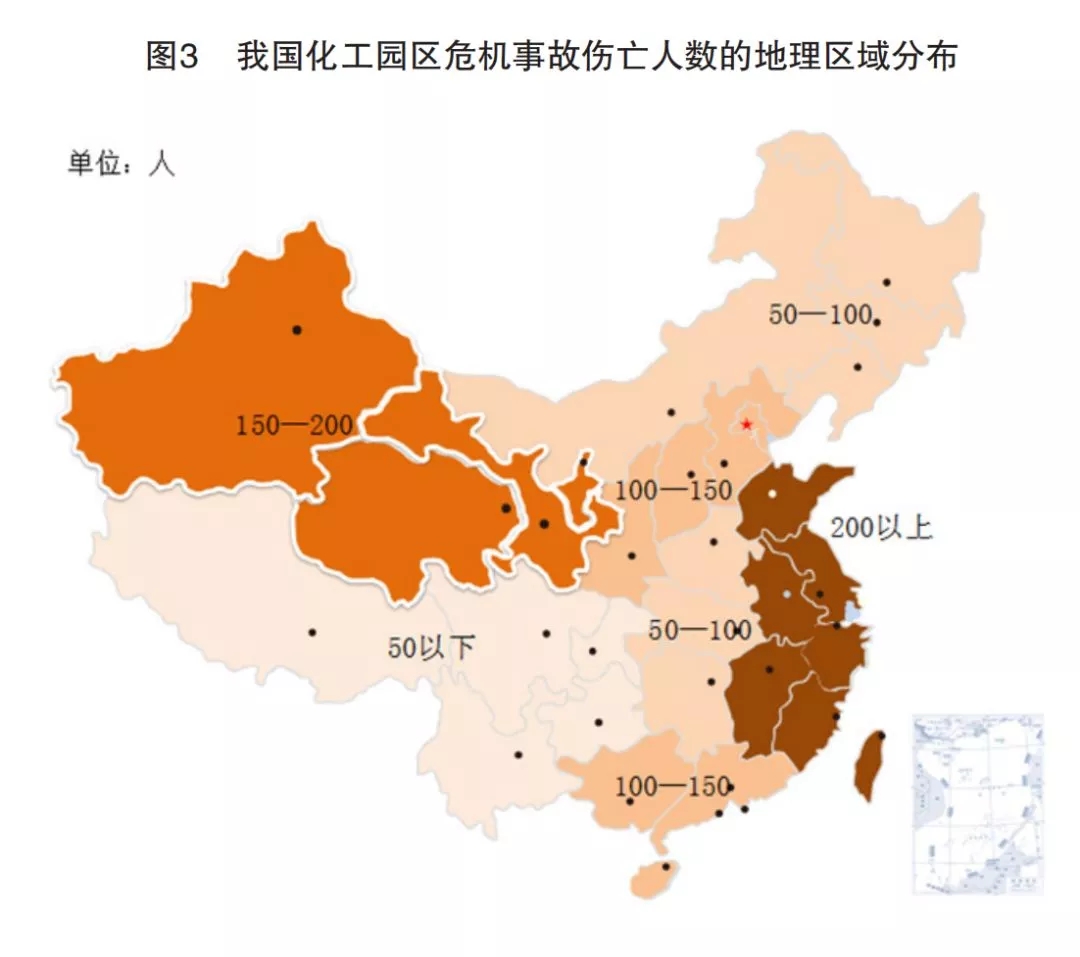
From the overall spatial layout, the chemical industry parks and their crisis accidents are mainly distributed in the northwest and coastal areas, and the east-west, South-North show a serious imbalance. In-depth analysis can be found that the regional distribution of chemical industry parks and crisis accidents is inconsistent, that is, the excessive number of parks is not the only decisive factor leading to frequent crises.
Summary: In addition to the internal risk-driven, that is, the significant increase in the number of chemical parks, there are also external risk-driven, that is, the inadequate investment in emergency management and the general weak awareness of crisis response.
3. Viewed from the status of rank
China's chemical parks are divided into three levels: national level, provincial level and provincial level. The emergency resources of different levels of parks are different, so the casualties are also quite different.
Among them, the crisis situation in provincial parks is the most serious, with 971 casualties and 114 accidents, with an average casualty loss of 8.52 persons per unit accident.
The number of casualties in the National Chemical Parks was 562, with 77 accidents, with an average casualty of 7.30 persons per unit.
The situation in the chemical industry parks below the provincial level is optimistic, with only 60 casualties and 12 accidents, with an average of 5 casualties per unit.
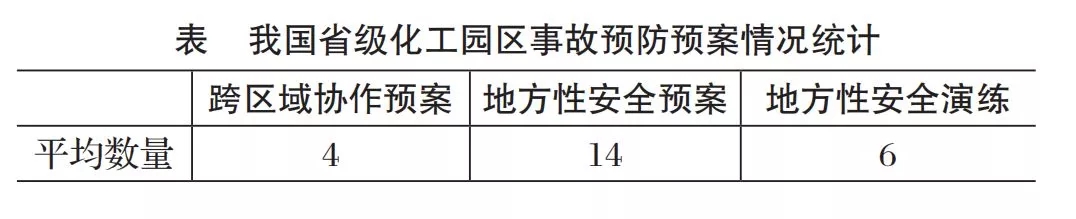
The system analysis of provincial parks with the most serious crisis accidents shows that the average number of local safety plans issued in 2017 is 14 (see table), while the number of drills for these safety plans is only 6. In addition, the implementation of cross-regional cooperation programs is seriously inadequate, only 4.
Summary: Compared with the United States, Japan and other developed countries, China's Chemical Park crisis prevention and early warning program is seriously lacking.
Revealing the Truth of Major Crisis in Chemical Industry Park from Four Perspectives
The focus of crisis accident management in chemical industry parks in China is mainly from three perspectives: emergency resource reserve, emergency resource dispatch, recovery and reconstruction, forming a circular rescue system: ldquo; pre-event-in-event-after-event-rdquo.

However, it is incomplete to avoid major crisis losses in chemical industry parks only by proceeding with the evolution process of the vertical development of the state. What are the real factors causing the major crisis in China's chemical industry parks? We analyze from these four perspectives:
1. Macroscopic Perspective: Unbalanced Park Layout Planning
The location selection theory of public facilities puts forward that the rational layout and scientific allocation of public facilities are the important foundation and necessary way to maximize service efficiency.
At present, the overall spatial layout of chemical industry parks in our country appears as ldquo; east-west, South-North & rdquo; uneven distribution, and the safety distance with vulnerable environment such as residential areas and freshwater sources is seriously insufficient, which makes the major crisis event once it breaks out, it will quickly spread to the surrounding areas. For example, in 2013-ldquo; 11-middot; 22-rdquo; the leakage of crude oil from Sinopec East Yellow Oil Pipeline into the municipal drainage canal, making Jiaozhou BayIt was heavily polluted.
The unbalanced spatial distribution of chemical industry parks makes it impossible for the government to form a unified response system. Most of the site selection ignores the problem that the high risks in the concentrated areas of chemical industry enterprises do not match the emergency response capacity. For example, the total number of large chemical industry parks in the eastern coastal provinces and cities (including the Yangtze River Delta, the Pearl River Delta, Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei) accounts for more than 70% of the whole country, and the incidence of crisis accidents exceeds that of the whole country. More than 50% in the northwest and central regions.
In addition, the incompatibility between the economic development and the crisis management ability of chemical industry parks has also become an important reason for the spread of accidents.
2. Medium-level perspective: insufficient cross-regional emergency linkage
Crisis accidents in chemical industry parks are highly uncertain, and the material flow and energy flow transfer are fast. Once they occur, it is difficult to accurately assess their development trend and disaster severity. The traditional emergency response system focuses on Crisis Management in a specific administrative region, and its implementation targets are limited to a specific subject, such as local risk identification and assessment, emergency materials reserve and allocation in the park, and emergency team construction in various provinces and municipalities.
However, the application of all kinds of science and technology and the implementation of local policies have not effectively alleviated the serious consequences of crisis accidents in chemical industry parks.
There are two reasons:
First, the crisis in the chemical industry park happens suddenly, and managers can not predict the severity of the situation accurately in advance. Once the emergency resource scheduling is difficult, they need the support of all parties, & ldquo; independent operation & rdquo; will greatly weaken the effect of crisis management, & ldquo; 8 & middot; 12 & rdquo; Tianjin Port Ruihai Company dangerous goods warehouse fire and explosion accident is a typical case.
Second, with the development of regional integration, the degree of integration between regions is getting higher and higher, and public emergencies in any place are likely to affect the surrounding areas. At present, the cooperation among chemical parks in China is rare, and the linkage emergency mechanism between provinces and cities in chemical parks is inadequate, which greatly increases the challenge of emergency work.
3. Micro-perspective: the infrastructure of the park does not match the scale of operation
The frequent occurrence of crisis accidents in chemical industry parks may be due to their specific geographical location, geological structure or climatic environment-ldquo; natural disasters-rdquo; induced by economic activities, production activities and interpersonal and social contradictions-ldquo; man-made disasters-rdquo; and more likely due to the special nature of high concentration of hazards in chemical industry parks and its infrastructure does not match. The rapid spread of disasters has resulted in huge property losses, physical and mental injuries and natural environmental pollution, such as the chlorine leakage accident in Jiangbei Chemical Park of Jilin Petrochemical Company in 2005.
Infrastructure problems include imperfect fire and electricity protection facilities, unreasonable storage of dangerous goods and obstacles to traffic network in the park.
In addition, the high density of enterprises is also a major problem facing China's chemical industry parks. If the number of enterprises is too large, a certain scale of chemical industry parks will appear-ldquo; saturation-rdquo; state, public emergency resources will be overused, which increases the possibility of crisis accidents and makes the crisis response unable to be reasonably guaranteed.
4. Government Regulation: Institutional Development and Policy Guidance Imperfect
In response to the crisis in the chemical industry park, the government should not only participate in the rescue work, but also play a guiding, controlling, promoting and intervening role of relevant policies and regulations in response to the crisis. Our government usually builds emergency prevention and early warning mechanism through safety plan and plan exercise. At this stage, our country has issued some emergency plans, but there are few safety plans for chemical industry parks. On this basis, crisis response rehearsal exercise activities are rare.
Crisis accidents in chemical industrial parks are explosive, and the disaster situation changes rapidly. When facing the crisis accidents in chemical industrial parks, the emergency subjects usually have problems such as lack of experience in dealing with them, inexperience in emergency command and rescue work and so on, so that they can not control the disaster situation in time.
Four Levels to Improve Safety Management of Chemical Industry Park
Chemical industry parks are the product of modern industry conforming to the development trend of resource intensive, internationalization of operation and maximization of benefits.
On the one hand, it is conducive to adjusting China's chemical industry structure, improving industrial concentration and enhancing industrial competitiveness, and plays an important role in resource optimization, waste management and sustainable development of the industry. On the other hand, dangerous sources are highly concentrated in chemical industry parks. These hazards are various, large-scale and densely reserved, which can easily lead to crisis accidents.
Therefore, the safety management of chemical industry park is particularly important. So what aspects should we start with?
1. Reasonably adjust the spatial layout of the park to form a balanced development situation.
The spatial layout planning of chemical industry parks is not only a traditional land use planning problem, but also a complex and systematic project, which requires the government departments to build a comprehensive, systematic and conform to the overall layout of the practical program, to guide the coordinated development of the park as a whole.
In view of the coastal areas with frequent crisis accidents in chemical industry parks, quantitative risk assessment should be carried out to balance the relationship between the development of chemical industry parks and the emergency protection of chemical industry parks, and to find a balance point. The layout of chemical industry parks in coastal areas should be designed pertinently, innovatively and effectively to achieve safe and balanced development.
In addition, on the basis of national layout planning, the location of chemical parks in each region should also take into account the convenience of emergency rescue traffic, the sufficient safe distance from residential areas, and the direction of waste sewage.
Finally, we should add a matching emergency platform and emergency agencies to realize the feasibility of macro-monitoring decision-making and dispatching command, so as to eliminate dangerous accidents in the bud.
2. Establishing regional emergency rescue linkage mechanism to ensure resource sharing
Interregional collaboration is conducive to the development of emergency rescue work. The government should build a cross-regional emergency linkage mechanism to improve the emergency rescue capacity of the region, which is of great significance in dealing with major crisis accidents.
Firstly, we should adhere to the principle of interest guidance, conduct regional risk survey and monitoring, effectively stimulate the enthusiasm and initiative of the participants in various regions, and enhance the awareness of regional cooperation and the ability of collaborative development.
Second, the key to the effective implementation of regional linkage mechanism lies in the region.The integration of regional vertical subjects (provinces, cities, counties) and horizontal subjects (provinces and cities) and the construction of multi-win-win and hierarchical response cooperation network based on this principle, such as the construction of cross-border trust and mutual respect of regional emergency cooperation relationship on the geographic basis, and the formation of emergency rescue linkage between participants sharing material, information, knowledge and emergency team resources. In the real sense, & ldquo; one side is difficult, the other side is helpful. & rdquo;.
Thirdly, the spatial boundary demarcation of cross-regional emergency cooperation should be determined according to geographical location, local emergency response capacity and the status quo of crisis in the park, not only according to the criteria of Administrative Region demarcation.
While emphasizing the sharing of emergency resources in large regions, we should consider whether it is operable or not. Therefore, besides guaranteeing the unification of regional cooperation management system at the macro level, we should also give each cooperation region certain autonomy according to the specific situation, so as to achieve the combination of & ldquo; Centralization & rdquo; and & ldquo; Authorization & rdquo; and so on.
3. Guiding the construction and operation of the park scientifically to prevent the occurrence of safety accidents
Firstly, the scale and number of enterprises in chemical industry parks should be rationally planned. On the one hand, in order to make full use of the park resources and improve the efficiency output of the park, park managers try to attract more enterprises to enter the park.
On the other hand, the existence of a large number of chemical enterprises will inevitably increase the incidence of safety accidents. Park managers should balance the relationship between the two, scientifically formulate the density of enterprises in the park, and form written regulations, so as to make appropriate adjustments to the chemical industry parks already built and under preparation.
The second is to raise the threshold of admission and establish a system of census, declaration and registration of major hazards.
Third, in the context of major disasters and accidents, in order to meet the emergency needs of the park, in addition to providing the necessary financial and material support, we can also start from the construction of emergency rescue team to promote rescue work.
We will improve the professional level of emergency rescue for staff, further expand the scale of rescue teams, strictly control the quality and quantity of rescue workers, enhance the disposal capacity of emergency teams, including public security fire brigades, special engineering rescue teams and medical rescue teams, and provide manpower support for park rescue.
4. Completely improve the emergency plan system and promote long-term rescue mechanism
Firstly, we should strengthen emergency supervision and management, improve the weak links of safety plans in chemical industry parks, promote the openness and transparency of emergency plans, formulate, update and revise safety plans in time, and conduct related rehearsals regularly in view of various accident risks, so as to improve the management ability of emergency rescue sites and reduce the losses caused by safety accidents.
Second, we should pay attention to practical results, increase the strategic framework of crisis management at the national level in chemical industry parks, and use the combination of national unified supervision standards and local characteristic supervision standards to conduct efficient command of emergency work.
Thirdly, we should strengthen public opinion guidance and emergency propaganda. By producing and issuing text manuals with concise content, easy to understand, easy to remember and use, we should conduct emergency training for enterprises in chemical industry parks and residents around chemical industry parks, make comprehensive use of traditional information channels such as television and radio, highlight the construction of new media propaganda platforms such as the Internet, and consult and conduct consultations with relevant personnel. Guidance, so as to enhance the emergency management awareness of all parties, enhance the ability of all parties to save themselves and others, and further reduce the serious consequences of crisis accidents.
(Source: Xingyuan Research, if there is any infringement, please contact and delete)





