
Central circulation tube evaporator
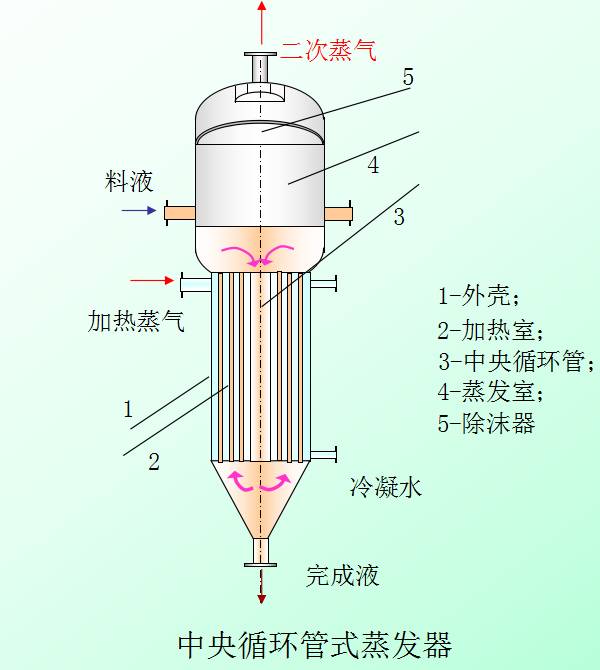
1, principle:
The central loop tube evaporator of the heating chamber from the heating tube of a vertical (boiling bundle), with a larger diameter of the tube bundle in the center, known as the central circulation pipe, the cross-sectional area is generally the heating tube cross-sectional area 40~100%.
When the heating medium inlet pipe heating, the heating area of the heating area of the heating tube unit is greater than the volume of liquid liquid in the pipe central circulation, so the relative density of the liquid in the tube is heated, causing the heating pipe and the central pipe circulation liquid density difference, the density difference between the solution drop tube the central circulation, then by heating tube natural circulation rising.
The circulation velocity of the solution depends on the density difference of the solution and the length of the tube. The greater the density difference is, the longer the tube is, the larger the circulating velocity of the solution is. But this kind of evaporator due to the total height limit, heating tube length is shorter, generally 1~2m, diameter 25~75mm, length diameter ratio of 20~40.
2, advantages: compact structure, easy to manufacture, good heat transfer, reliable operation.
3, disadvantages: circulation speed below 0.4~0.5m/s, cleaning and maintenance inconvenient.
Two, hanging basket type evaporator
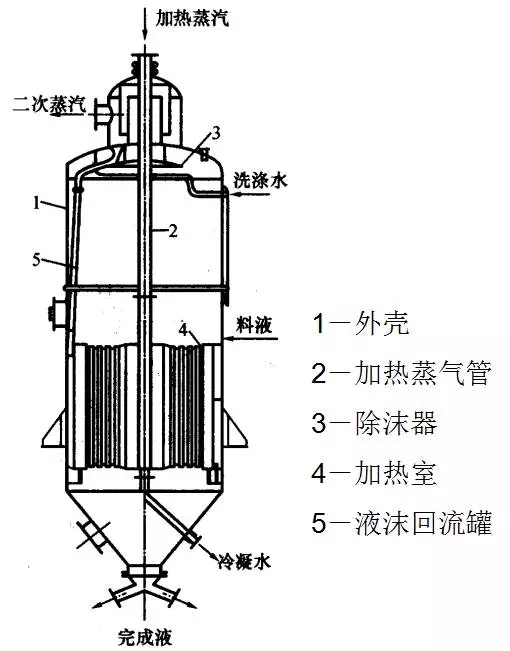
1, advantages: circulation speed can be slightly larger, easy to overhaul, less heat loss.
2, disadvantages: complex structure, unit heat transfer surface metal consumption.
3, applicable: easy crystallization, scaling solution evaporation.
Four, external heat type evaporator
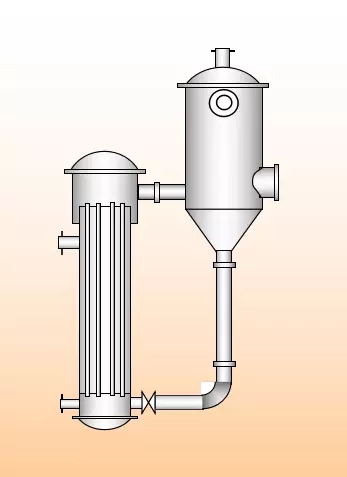
1, principle:
The utility model is characterized in that the heating chamber is separated from the separation chamber, which is not only convenient for cleaning and replacing, but also can reduce the total height of the evaporator. Because of the heating pipe (longer lengths and diameters ratio 50~100) at the same time, because the solution in the circulation pipe is not heated, so the solution circulation rate, up to 1.5m/s.
2, advantages: reduced evaporator height, easy to clean and replace, circulation speed is bigger.
Five, Levin evaporator
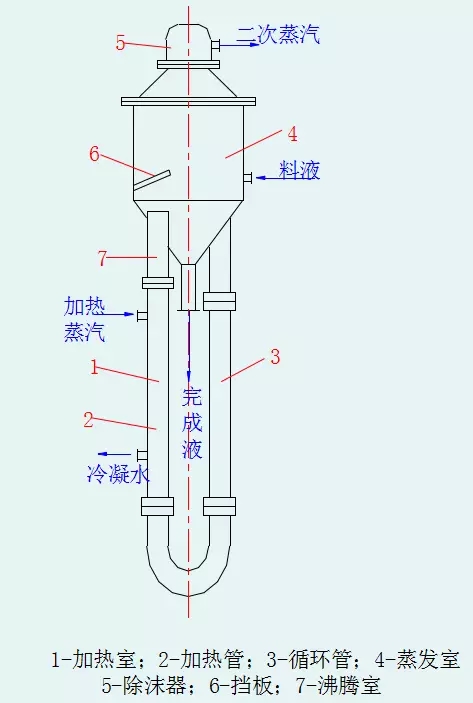
1, principle:
The structure characteristics of Levin evaporator is on the upper part of the heating chamber is additionally provided with a boiling chamber. Thus, the solution in the heating chamber can be vaporized only when the liquid column is added to the boiling chamber. A longitudinal baffle is arranged above the boiling chamber to prevent the bubble from growing up. In addition, because the circulation tube is not heated, the solution circulation impetus is bigger. The height of the circulating pipe is generally 7~8m, and its cross-sectional area is about 200~350% of the total cross-sectional area of the heating pipe. Thus the flow resistance of the circulation tube is small, the circulation speed can be as high as 2~3m/s.
2, advantages: gasification in boiling room, circulation speed is large, help to reduce or avoid heating tube surface crystallization and scaling, heat transfer effect is good.
3, disadvantages: loss of temperature, equipment, large consumption of materials, the need for large factories.
Six, forced circulation evaporator
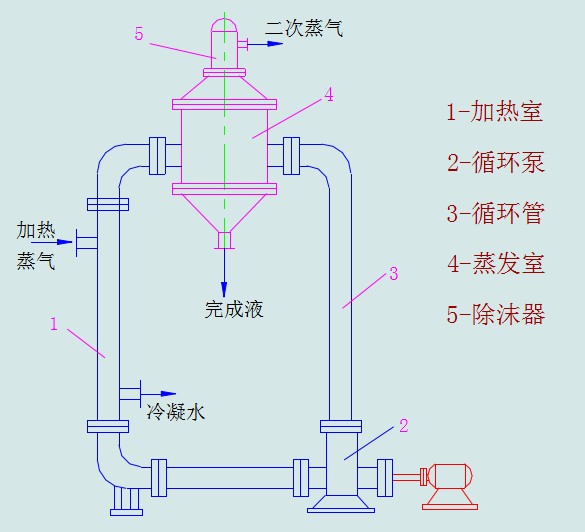
1, advantages: suitable for large viscosity, Yi Jiejing, easy scaling material evaporation circulation speed can be adjusted, larger heat transfer coefficient.
2, disadvantages: energy consumption.
Seven, one way type evaporator
1, characteristics: solution in the form of liquid membrane once through the heating room, not cycle.
2, advantages: short residence time of solution, which is especially suitable for heat sensitive materials evaporation; temperature difference loss of surface heat transfer coefficient is larger.
3, disadvantages: design or operation is not easy to film, heat flow will be significantly reduced; not suitable for easy crystallization, scaling material evaporation.
(a) rising film evaporator
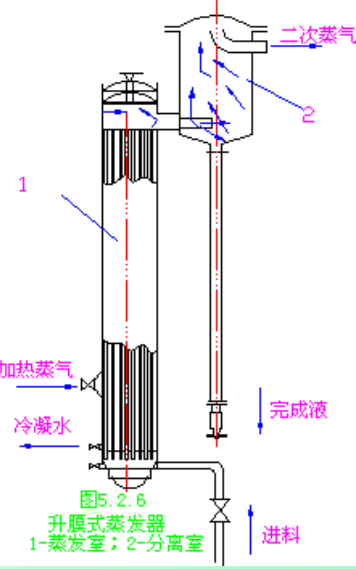
(1) principle:
Rising film evaporator heating chamber by one or a plurality of long vertical tubes, usually the heating pipe diameter is 25~50mm, length and diameter ratio of 100~150. The raw material liquid enters the bottom of the evaporator after preheating, and the heating steam condenses outside the tube.
When the solution is heated and vaporized rapidly, the generated two steam rises rapidly in the pipe, and drives the liquid to flow upward along the inner wall of the pipe. Therefore, the solution from the bottom of the evaporator rose to the top of the process gradually evaporated, concentrated solution into the separation chamber and two steam separation from the bottom of the separator. Under normal pressure heating pipe outlet two steam speed should not be less than 10m/s, generally 20~50m/s, decompression operation, sometimes up to 100~160m/s or higher.
(2) performance characteristics: a rising film evaporator applicable to larger evaporation (i.e. dilute solution), heat sensitive and easily foaming solution, but is not suitable for high viscosity solution, crystal precipitation or easy scaling.
(two) falling film evaporator
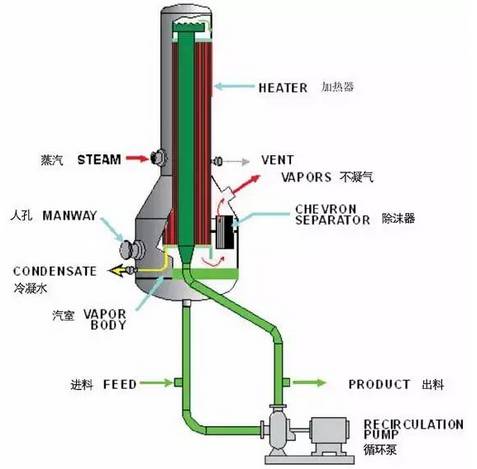
(1) principle:
The difference between the falling film evaporator and the rising film evaporator is that the raw material liquid is added from the top of the heating pipe. The solution of inner tube membranous along the downstream under its own gravity, and evaporation, vapor liquid mixture by heating at the bottom of the tube into the separation chamber, after gas-liquid separation, liquid discharged from the bottom of the separator.
In order to make the solution uniform on the wall, a liquid membrane filter is needed at the top of each heating pipe. There are a variety of cloth membrane type, three kinds of commonly used, a spiral groove of the cylinder as the diversion pipe, the liquid distribution in the downstream rotation along the trench on the inner wall of the diversion pipe pipe; the lower part is a cone, the cone bottom of the inner concave, lest along the inclined surface of the cone body under the stream of liquid to liquid is central; through the slot wall film like drop along the heating pipe.
(2) advantages: high heat transfer coefficient, compared with the rising film, can evaporate higher concentration of the solution, the viscosity of the larger material can also be applied.
(3) disadvantages: complex structure.
(three) direct contact heat transfer evaporator
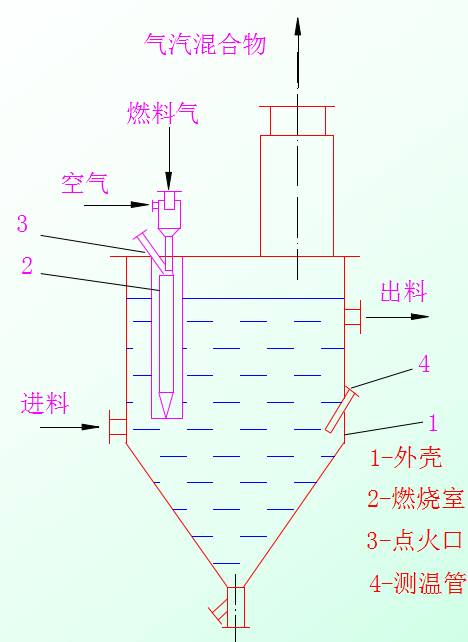
1 advantages: simple structure, suitable for easy crystallization, easy scaling and evaporation of corrosive materials. Good heat transfer effect, high heat utilization.
(2) disadvantages: not applicable to non smokeTreatment of air pollution materials, and two steam utilization is limited.
Eight, horizontal evaporator
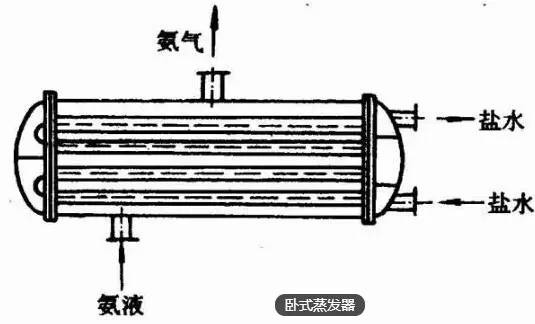
1, principle:
It is similar to the structure of horizontal shell and tube condenser. According to the liquid supply mode can be divided into shell tube evaporator and dry evaporator two kinds. Horizontal shell and tube evaporator is widely used in closed brine circulation system.
2, performance characteristics:
Compact structure, good contact between liquid and heat transfer surface, high heat transfer coefficient. But it needs to fill a lot of refrigerant, liquid column to evaporation temperature will have certain influence. And when the concentration of Saline Brine Pump for reducing or stopping, saline frozen in tube. If the refrigerant freon, lubricating oil is difficult to return the dissolved Freon compressor. Also need to stop cleaning work.
Nine, spiral tube evaporator

1, principle:
Common vertical tube and spiral tube evaporator is the evaporation of the refrigerant in the tube, the entire evaporator tube immersed in the refrigerant laden group Sheng (or in the pool and the tank), in order to ensure the refrigerant cycle at a certain speed in the box, box is welded with a longitudinal baffle and a screw stirring device. The coolant flow rate is 0.3 ~ 0.7m/s, in order to enhance heat transfer.
2, performance characteristics:
Vertical tube and spiral tube evaporator can only be used in the open cycle system, the refrigerant must be non volatile substances, commonly used is saline and water etc.. Such as brine, evaporator tube easily oxidized, and salt water easy to absorb moisture and reduce concentration. The two evaporator can directly observe the flow of refrigerant, is widely used in brine system with ammonia as refrigerant.
Ten, cooling pipe
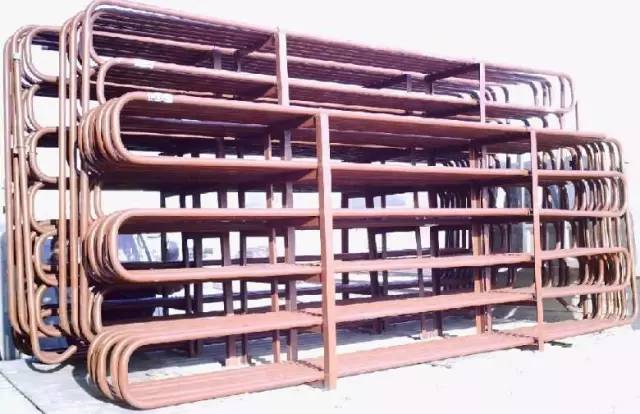

1, principle:
Cooling tube is an evaporator for cooling air. Widely used in cryogenic storage, the refrigerant flows and evaporates in the cooling pipe, as the heat transfer medium, the cooling air is used as natural convection.
2, performance characteristics:
The biggest advantage of the cooling pipe is simple structure, easy to manufacture, the storage of non packaged food in the warehouse caused by less dry consumption. But the heat transfer coefficient is low, and the defrosting operation is difficult, which is not conducive to automation. For seamless steel pipe welding with direct ammonia cooling system, the light tube or winding finned tube; the Freon system, mostly by winding or finned copper tube and fin tube group.
Eleven, MVR falling film evaporator

1, principle:
The material liquid from the heat exchanger tube box, through the liquid distributor of the material assigned to each heat exchange tube, and along the inner wall of the heat exchanging pipes to form uniform liquid film, the liquid in the tube membrane in the downflow is in the process of heating steam heating shell, an edge to edge and boiling evaporation. To the heat exchanger tube bottom material into concentrate and two steam.
The concentrate falls into the lower tube, and the two vapor enters the gas-liquid separator. In gas-liquid separator two steam entrained liquid droplets are removed, conveying two pure evaporation from the separator to the compressor. The compressor compresses the two steam as the heating steam and transfers it to the heat exchanger shell for evaporator heat source. Continuous evaporation process.
2, performance characteristics:
(1) heat transfer efficiency is high.
(2) small area.
(3) short time of material stay, not easy to cause material deterioration.
(4) suitable for higher viscosity materials.
3, the scope of application:
Falling film evaporator for MVR evaporation crystallization process of pre concentration process, the viscosity of the material can be evaporated, especially suitable for heat sensitive materials, but not for the treatment of crystal materials.
Twelve, MVR forced circulation evaporator
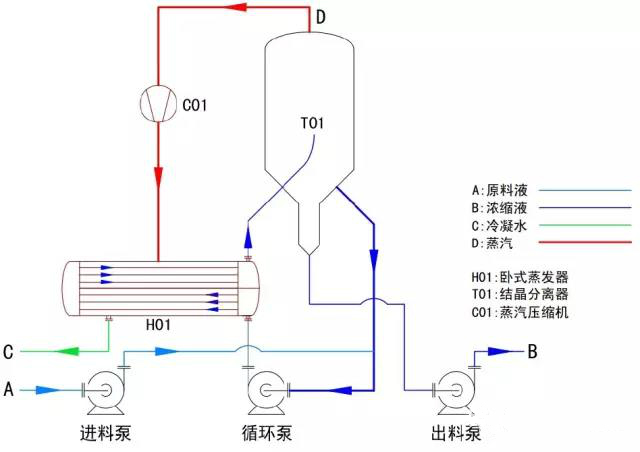
1, principle:
Forced circulation evaporator consists of evaporation separator, heat exchanger and forced circulation pump. The heating temperature of the material in the heat exchange pipe of the heat exchanger is increased outside the heat exchange pipe. Under the action of the circulating pump, the material rises to the evaporation separator, and the evaporation of the material causes the evaporation of the material in the evaporation separator.
Evaporate two steam overflow from the material, the material is concentrated over saturate and the crystal growth, lifting the saturated material into the forced circulation pump, into the heat exchanger in the circulating pump under the action of the material this cycle evaporation or concentration crystallization.
Output of slurry pump from circulating pipe. For the two time in the steam evaporation separator after the separation and evaporation separator defoaming device after purification, transported to the compressor, compressor to two times compressed vapor transported to the heat exchanger used as an evaporator heating steam and realize continuous evaporation heat circulation.
2, performance characteristics:
(1) lower heat transfer coefficient.
(2) heat transfer surface is not easy to form scaling or crystallization.
3, the scope of application:
Suitable for easy scaling, crystallization, high viscosity material evaporation concentration or evaporation crystallization process.
Thirteen, MVR evaporation OSLO crystallizer
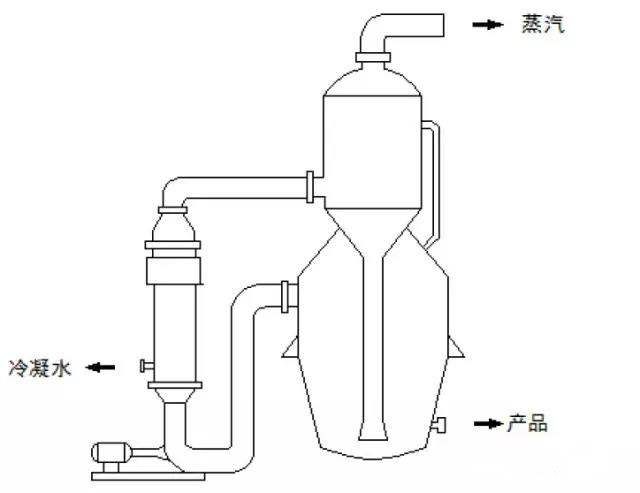
1, principle:
OSLO evaporation crystallizer consists of OSLO evaporator, heat exchanger and forced circulation pump. The heating temperature of the material in the heat exchange pipe of the heat exchanger is increased outside the heat exchange pipe. Under the action of the circulating pump, the material rises to the OSLO evaporation crystallizer, and the material evaporation occurs in the OSLO evaporation crystallizer due to the static pressure drop.
Evaporate two steam overflow from the material, the material is concentrated to produce satiety, supersaturated solution in OSLO evaporation crystallizer center tube decreased with small crystalline solution in full contact and make further crystallization growth, larger crystal growth after the crystallization precipitation elutriation column elution column below to elutriation pumping crystal to the thickener. Smaller crystals continue to grow in OSLO crystallizer.
The clarified liquid is forced to circulate to the heat exchanger to continue heating, and the material is evaporated and condensed or condensed gradually. The two steam in the OSLO evaporation crystallizer is transported to the compressor after the separation and defoaming device is purified on the upper part of the separator. The compressor transports the two steam to the heat exchanger shell to be used as the evaporator to heat the steam. Realize thermal circulation continuous evaporation.
2, the main features:
(1) large crystal size and uniform particle size.
(2) large equipment and high cost.
3,Scope of application: suitable for the production of material with larger crystal size.
Process equipment network finishing release, please indicate the source reprint.














